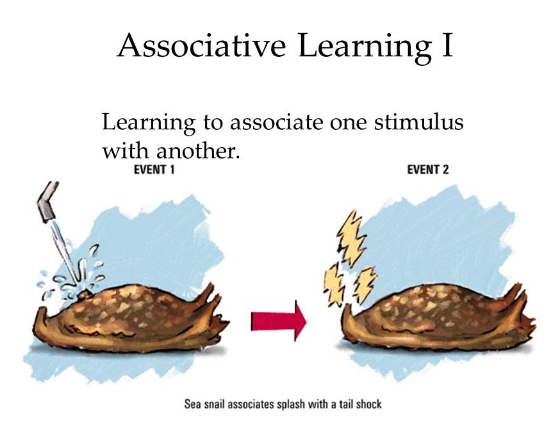
Associative learning is a fundamental process in which our brains make connections between different stimuli or events. Understanding the basics of associative learning can provide insight into how we learn and remember information.
What is Associative Learning?
Associative learning is a type of learning that involves linking two or more stimuli or events together. It is based on the idea that our brains are constantly forming connections between different pieces of information based on their relationship to each other.
Types of Associative Learning:
There are two main types of associative learning: classical conditioning and operant conditioning. In classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus is paired with a meaningful stimulus to create a learned response. In operant conditioning, behaviors are reinforced or punished to increase or decrease their likelihood of occurring again.
How Does Associative Learning Work?
Associative learning works through a process of trial and error. When a neutral stimulus is paired with a meaningful stimulus, our brains form a connection between the two. Over time, this association becomes stronger, leading to the learned response.
Example of Associative Learning:
A classic example of associative learning is Pavlov’s experiment with dogs. In this experiment, Pavlov paired the sound of a bell with the presentation of food. Eventually, the dogs began to salivate at the sound of the bell alone, demonstrating that they had formed an association between the bell and the food.
Applications of Associative Learning:
Associative learning is used in a variety of contexts, including education, therapy, and marketing. By understanding how our brains make connections between stimuli, we can tailor learning experiences to be more effective and impactful.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of associative learning can provide valuable insights into how our brains make connections and learn new information. By recognizing the role of associative learning in our everyday experiences, we can enhance our ability to learn and remember information more effectively.